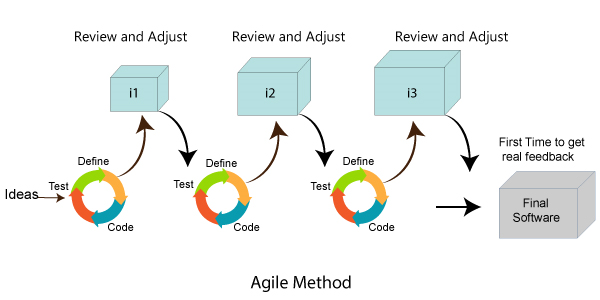
Advantage of Agile MethodologyThere are various advantages of using agile methodology over traditional waterfall model or others. Agile development methodology and testing practices have worked wonders for numerous organizations with positive aspects. Its positive aspects are not hidden, it is very much visible in the organization.Advantages of Agile Methodology
 Disadvantages of Agile methodology:
Advantages of the Waterfall Model:
 Disadvantages of Waterfall Model:
Compression between the Agile methodology and Waterfall model:
|
Friday, February 21, 2020
Advantage of Agile Methodology
Advantages, Disadvantages of Agile
Advantages of Agile
model:
- Customer
satisfaction by rapid, continuous delivery of useful software.
- People
and interactions are
emphasized rather than process and tools. Customers, developers and
testers constantly interact with each other.
- Working
software is delivered frequently (weeks rather than months).
- Face-to-face
conversation is the best form of communication.
- Close,
daily cooperation between business people and developers.
- Continuous
attention to technical excellence and good design.
- Regular
adaptation to changing circumstances.
- Even
late changes in requirements are welcomed
Disadvantages of
Agile model:
- In case of some software deliverables,
especially the large ones, it is difficult to assess the effort required
at the beginning of the software development life cycle.
- There
is lack of emphasis on necessary designing and documentation.
- The
project can easily get taken off track if the customer representative is
not clear what final outcome that they want.
- Only
senior programmers are capable of taking the kind of decisions required
during the development process. Hence it has no place for newbie
programmers, unless combined with experienced resources.
When to use Agile
model:
- When
new changes are needed to be implemented. The freedom agile gives to change is very
important. New changes can be implemented at very little cost because of
the frequency of new increments that are produced.
- To
implement a new feature the developers need to lose only the work of a few
days, or even only hours, to roll back and implement it.
- Unlike the waterfall model in agile model
very limited planning is required to get
started with the project. Agile assumes that the end users’ needs are ever
changing in a dynamic business and IT world. Changes can be discussed and
features can be newly effected or removed based on feedback. This
effectively gives the customer the finished system they want or need.
- Both system developers and stakeholders alike,
find they also get more freedom of time and options than if the software
was developed in a more rigid sequential way. Having options gives them
the ability to leave important decisions until more or better data or even
entire hosting programs are available; meaning the project can continue to
move forward without fear of reaching a sudden standstill.
Agile Methodology
AGILE:
It is a iterative and incremental approach.
The main goal of agile is customer satisfaction by quick delivery of
working software.
PRINCIPLE OF AGILE METHODOLOGY:
- Customer can change the requirement at any
point of development stage.
- Release should be short.
- There will be good communication between
customer, BA, developer and Test Engineer.
- It is simple model to adopt.
- Developers and test engineers will be doing
lot of meetings at regular intervals in order to improve the quality of
process.
What is agile testing?
Testing the software by following the principle of agile methodology is
called agile testing.
Types of agile methodologies?
1. Scrum methodologies
2. XP (Extreme Programming)
3. FDD (Feature driven development)
4. Crystal Clear
5. Lean and Kanban
6. ASDM (Adoptive Software Development Method)
7. DSDM (Dynamic Software Development Method)
Scrum methodologies/Scrum Process:
1. Release: Combination of sprints is called
release
2. EPIC: Complete set of requirement is called EPIC
One EPIC consist of multiple features or modules
User Stories/Stories/Story Cards:
Feature or modules or functionalities is called as Stories
One EPIC consist of multiple stories
Story Point:
It is rough estimation given developer and test engineer to develop and
test individual stories
Ex:
1 story point=9 hours
1 SP=6
1 SP=8
Story point should be in Fibonacci series
QA Story points estimated based on the following aspects:
Time spent on understanding story
Write test scenarios
Write test cases
Review test cases
Test case execution
Defect tracking
Developer Story points estimated based on the following aspects:
Understanding requirements
Design
Coding
Reviewing code
WBT
Time spent on fixing the defects
Swag:
The rough estimation given by developer and test engineer for every
individual stories in the form of hours
Sprint:
Sprint is the actual time spent by developers and test engineer to
develop and test one or more stories
Sprint planning:
Sprint planning is a meeting conducted by scrum master on the first day
every sprint
Explain the requirement
Identify list of task to be done
Assign task to engineer
Scrum Master:
Scrum master is a person who is responsible for delivery of the software
to the customer within a planned period of time.
Scrum master will tract all the activities done by developer, test
engineer and BA.
BA/Senior test engineer / senior developer /Project manager and even
customer can become Scrum Master.
Scrum Meeting:
It is a meeting conducted by a scrum master on the daily basis.
It is also called as daily stand up meeting
This meeting is strictly bounded for 15 to 20 minutes
In this meeting we discuss below mentioned points
- What you did yesterday
- What have you planned today
- Are there any obstacles or impediments
Sprint retrospective meeting
It is a meeting conducted by scrum master on the last day of every
sprint
In this meeting we discuss the following points
- What went well
- What didn’t go well
- Are there any actions plan
Release retrospective meeting
It is the meeting conducted by scrum master on the last day of every
sprint
Bug triage meeting:
This is the meeting conducted by the test engineer or scrum master a
week or 2 week before the release.
BA,TE,Developer and SM will be a part of meeting
In this meeting test engineer list all the open and pending bugs which
are not fixed by the developers in the current and previous release as a team
we will re prioritize the defect from the customers’ business point of view and
decide how many bugs should be fixed as part of a current release and how many
bugs can be move to upcoming release.
Product Backlog meeting:
This is a meeting conducted by a BA or SM a week or 2 week before the
release
In this meeting test engineer and developer come up with list all the
pending stories
Which are not implemented as part of the current and previous release.
As a team we will re prioritize all the stories from the business point
of view and decide how many stories can be in implemented in the current
release and how many stories can move to next upcoming sprint or
releases.
Chickens and Pigs:
Chickens are the set of people who are not actually committed to the project and they will not do any contributed towards the project where in they will get the business and get the work done by other people.
Ex: Customers, Stake holder and management team.
Pigs are the people who actually works on the project, committed to the project and contribute towards the project.
Ex: Test engg, Dev engg, Scrum master, BA etc.
WHAT IS A BURNDOWN CHART?
Chickens and Pigs:
Chickens are the set of people who are not actually committed to the project and they will not do any contributed towards the project where in they will get the business and get the work done by other people.
Ex: Customers, Stake holder and management team.
Pigs are the people who actually works on the project, committed to the project and contribute towards the project.
Ex: Test engg, Dev engg, Scrum master, BA etc.
WHAT IS A BURNDOWN CHART?
A burndown chart shows the amount of work that has been completed in an epic or sprint, and the total work remaining. Burndown charts are used to predict your team's likelihood of completing their work in the time available. They're also great for keeping the team aware of any scope creep that occurs.
Burndown charts are useful because they provide insight into how the team works. For example:
- If you notice that the team consistently finishes work early, this might be a sign that they aren't committing to enough work during sprint planning.
- If they consistently miss their forecast, this might be a sign that they've committed to too much work.
- If the burndown chart shows a sharp drop during the sprint, this might be a sign that work has not been estimated accurately, or broken down properly.
Resume points:
Experience:
Worked on Agile Scrum Development process.
Involved in Sprint planning meeting,Daily stand up meeting and
Sprint Retrospective meeting.
Fresher:
Excellent knowledge on Agile Scrum Development process.
Very good knowledge on Sprint planning meeting.
Very good knowledge on Scrum meeting.
Very good knowledge on Sprint Retrospective meeting.
Agile vs Waterfall
Waterfall challenges
Poor quality
Poor visibility
Too risky
Can't handle change
The Agile Approach
Quality improves because testing starts from day one.
Visibility improves because you are 1/2 way through the project when you
have built 1/2 the features.
Risk is reduced because you are getting feedback early, and
Customers are happy because they can make changes without paying
exorbitant costs.
The Sprint Review
Purpose
Sprint Review Meeting is all about demonstrating the work done and
gather the feedback and buy-in. At some places, the Sprint Review meeting is
also known as Sprint Demo. Sprint Review Meeting is usually done at the end of
the sprint but before the Sprint Retrospective meeting.
What are the disadvantages of the agile model?
Answer: Some of the disadvantages of using agile model are as follows:
a) Not easy to predict: When you encounter a large project, it is not
easy to get an idea how much effort will it need
b) If the guidelines given by the customers is not properly grasped,
then final outcome of the project is not customer satisfying
c) Sometimes focusing on design and documentation is not proper
d) High-level decisions are under the hand of Veterans, if not combined
with non-experienced one, freshers have little scope to grasp proper knowledge.
Thursday, February 20, 2020
TRACEABILITY MATRIX
TRACEABILITY
MATRIX
We have learnt about TM earlier. Once
the missing requirements are identified – we write the test cases for the requirements
which we have missed – review it and get it approved – and then store the test
cases in the repository and then fill in the name of the test case for which
the requirements have been missed.
Traceability Matrix is a document
which has got the mapping between requirements and test cases. We write TM to
make sure that every requirement has got atleast 1 test case.
|
Serial No.
|
Module Name
|
High Level Requirements
|
Detailed Requirement
|
Test Case Name
|
Automation Script Name
|
1
|
LOANS
|
1.1 Personal Loans
|
1.1.1 …
|
CBO_PL_Approval
|
|
1.1.2 …
|
CBO_PL_Elgibility check
|
||||
1.2 Home Loans
|
1.2.1 …
|
||||
1.2.2 …
|
|||||
2
|
AMOUNT TRANSFER
|
2.1 FAN text field
|
2.1.1 Should accept only 10 digit integer
|
…
|
|
2.1.2 Should accept only those numbers which are
created by manager
|
..
|
||||
2.2 TAN text field
|
2.2.1 Should accept only 10 digit integer
|
…
|
|||
2.2.2 Should accept only those numbers created by
manager
|
|||||
2.3 Amount Text field
|
2.3.1 Should accept only 100 - 5000, positive
integer
|
…
|
|||
2.3.2 Should not accept more than balance
|
|||||
…
|
…
|
…
|
…
|
…
|
In the above TM – we have written the
above TM looking at the requirements. For every requirement, we write the test
case name(given in the header of the test case) and thus we know that we have
written a test case for that particular requirement. Now, we block the cells
for which we have not written test cases. Thus we have missed out on these
requirements.
We block it in red. For whichever
requirement we have not written test case – we read the requirements – write
test cases – review it and get it approved – store it in repository – then go
fill in the test case name for whichever requirements we have missed. Thus, in
this way for every requirements we have atleast 1 test case.
Look at the figure in the next page,
Thus now all the blocked cells have
been removed and test cases have been written for the missing requirements.
Serial No.
|
Module Name
|
High Level Requirements
|
Detailed Requirement
|
Test Case Name
|
Automation Script Name
|
1
|
LOANS
|
1.1 Personal Loans
|
1.1.1 …
|
CBO_PL_Approval
|
|
1.1.2 …
|
CBO_PL_Elgibility check
|
||||
1.2 Home Loans
|
1.2.1 …
|
…
|
|||
1.2.2 …
|
…
|
||||
2
|
AMOUNT TRANSFER
|
2.1 FAN text field
|
2.1.1 Should accept only 10 digit integer
|
…
|
|
2.1.2 Should accept only those numbers which are
created by manager
|
…
|
||||
2.2 TAN text field
|
2.2.1 Should accept only 10 digit integer
|
…
|
|||
2.2.2 Should accept only those numbers created by
manager
|
…
|
||||
2.3 Amount Text field
|
2.3.1 Should accept only 100 - 5000, positive
integer
|
…
|
|||
2.3.2 Should not accept more than balance
|
…
|
||||
…
|
…
|
…
|
…
|
…
|
But 100% coverage is not assured in
Traceability matrix. For ex, a
requirement may have about 10 scenarios, but we have covered only 3 scenarios.
Thus, TM will not promise you that we have 100% coverage. Instead it ensures
that every requirement has atleast 1 test case which in turn gives the
confidence that we are touching all the features atleast once.
In the above table, we have a column
named automation script name. If we
are automating any test case, we fill in the automation script name (which is
same as manual test case name) and which we are not converting, we write it as
manual. Thus, we can know which test case is automated and manual. We write
this because we cant check every test case to see if it is manual or automated.
This is shown in the table given below,
Serial No.
|
Module Name
|
High Level Requirements
|
Detailed Requirement
|
Test Case Name
|
Automation Script Name
|
1
|
LOANS
|
1.1 Personal Loans
|
1.1.1 …
|
CBO_PL_Approval
|
CBO_PL_Approval
|
1.1.2 …
|
CBO_PL_Elgibility check
|
CBO_PL_Elgibility check
|
|||
1.2 Home Loans
|
1.2.1 …
|
…
|
..
|
||
1.2.2 …
|
…
|
…
|
|||
2
|
AMOUNT TRANSFER
|
2.1 FAN text field
|
2.1.1 Should accept only 10 digit integer
|
…
|
Manual
|
2.1.2 Should accept only those numbers which are
created by manager
|
…
|
Manual
|
|||
2.2 TAN text field
|
2.2.1 Should accept only 10 digit integer
|
…
|
…
|
||
2.2.2 Should accept only those numbers created by
manager
|
…
|
…
|
|||
2.3 Amount Text field
|
2.3.1 Should accept only 100 - 5000, positive
integer
|
…
|
…
|
||
2.3.2 Should not accept more than balance
|
…
|
Manual
|
|||
…
|
…
|
…
|
…
|
…
|
TM gives traceability from high level
requirements to automation script name.
Advantages of
Traceability Matrix
·
Ensures
that every requirement has atleast 1 test case
·
If
suddenly requirement is changed – we will be knowing which is the exact test
case or automation script to be modified
·
We
will come to know which test case should be executed manually and which are to
be done automatically.
Who writes
Traceability Matrix?
Test Lead gives an empty template and
Test Engineer fills it up for his respective modules. Each Test Engineer fills
it up for their modules. For ex, TE concerned with Loans feature will fill in
the details(test case names) for Loans feature. Similarly other TE(s) do for
their features.
Test Lead consolidates the report
after everything has been filled up.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
-
Question #1) One of the fields on a form contains a text box that accepts numeric values in the range of 18 to 25. Identify the invali...
-
Integration Testing: Testing data flow between dependent modules is called integration testing. INTEGRATION TESTING is defined as a ...
-
What is Software Testing Technique? Software Testing Techniques help you design better test cases. Since exhaustive testing is not possi...